According to the latest dietary guidelines, it is recommended to take 2,300 milligrams of sodium (1 tsp) daily. However, our average daily intake is estimated to be close to 3,400 milligrams of sodium (approximately 1 and 1/3 teaspoon).
Excessive salt intake can cause hypernatremia and lead to serious health problems over time. Crfat Sides has listed the most common signs that you are probably eating too much salt in your diet.
Signs You’re Eating Too Much Salt
7. Swelling
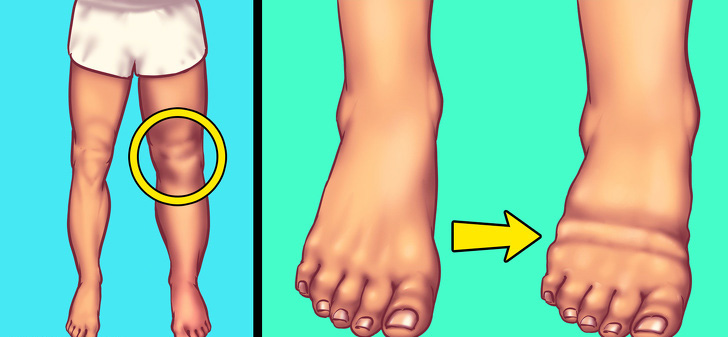
If your rings are a little tight, your feet are swollen, or your eyes are swollen in the morning, you are probably eating too much salt.
The condition in which your body begins to retain additional water as a result of high salt intake is called edema and must be treated with a very restricted diet.
6. Excessive Thirst
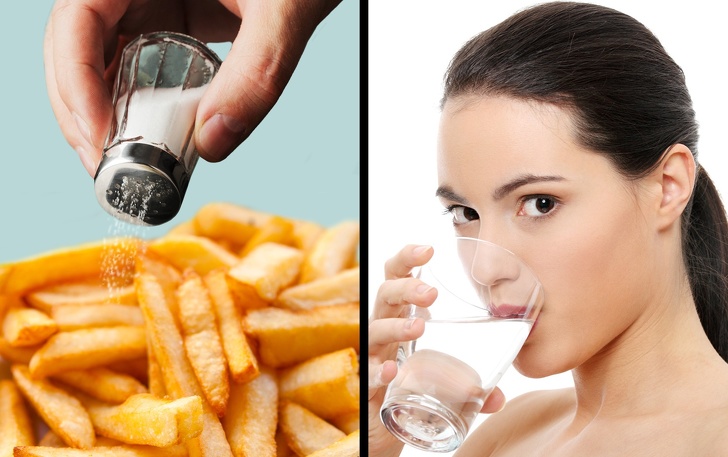

The sodium found in salt helps balance fluids in your body. When you eat too much salt, your body needs more fluids to help cleanse your system, so your muscles and other organs can function properly.
This is how your body corrects the water-sodium ratio, and drinking water is the best way to get things back to normal. Remember that not drinking enough water can force your body to draw fluid from your cells and this can cause you to become dehydrated.
5. Changes in Urination
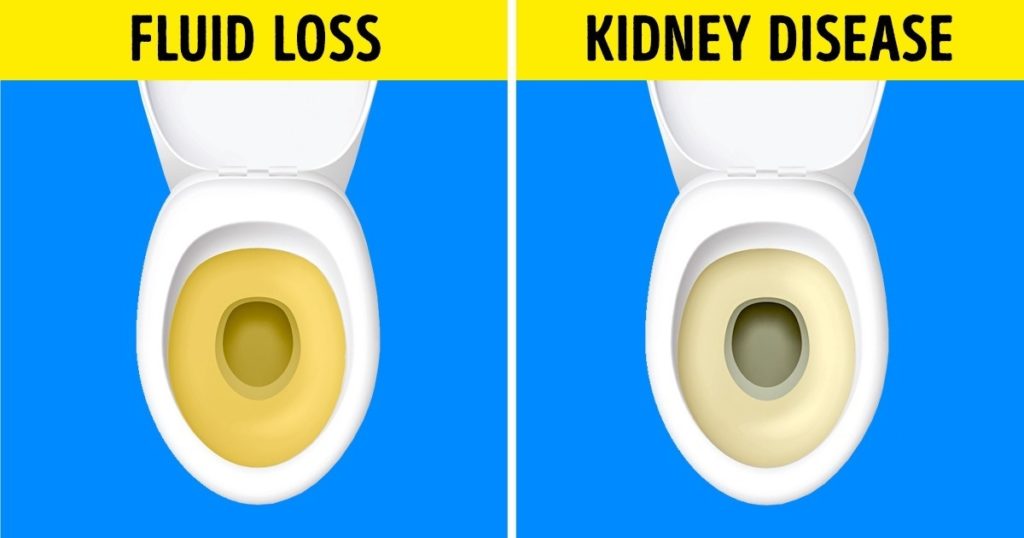
As a general rule, the accumulation of sodium in your body causes serious changes in urination that can occur for two reasons:
Consuming too much salt causes the kidneys to work overtime to eliminate it from the body. This can lead to kidney disease that generally makes urination more frequent with pee that appears transparent or completely clear.
Excessive consumption of sodium in the body can result from the loss of fluids that often lead to dehydration. When there is a significant loss of water in the body, urine output decreases and becomes thick and dark yellow.
4. Achy Bones
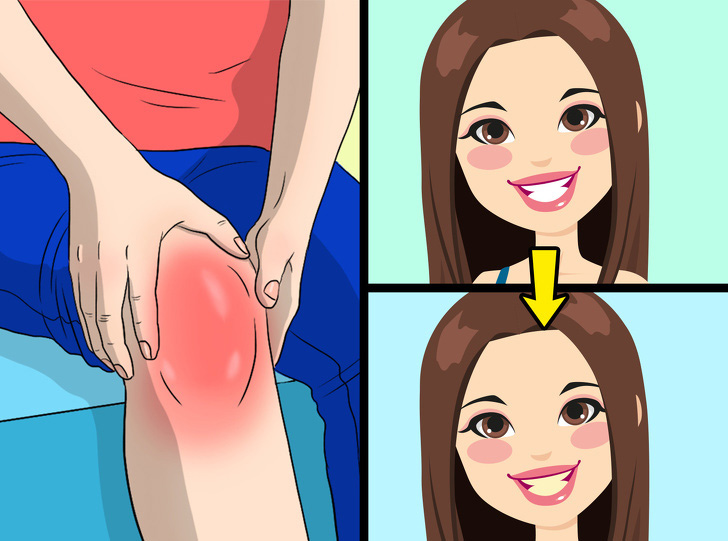
Salt intake can be a major obstacle to a sturdy skeleton. When you eat a lot of common table salt, your kidneys cannot completely release it, and this greatly increases calcium loss.
READ RELATED: 15 Proven Health Benefits Of Almonds: Nutrition, Side Effects, How To Eat And Other Details
Chronic calcium deficiency can lead to weak bones, tooth problems, and even cause osteoporosis.
3. Muscle Cramps
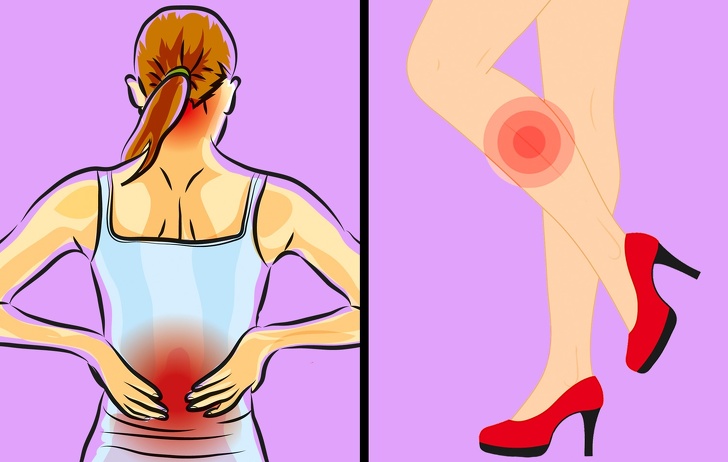
Maintaining the correct balance of sodium and potassium is crucial for your health since these chemical elements are responsible for muscle contraction. If you become unbalanced by overusing a salt shaker or consuming salty foods, you may experience cramps or muscle tightness and pain.
2. Persistent Headaches
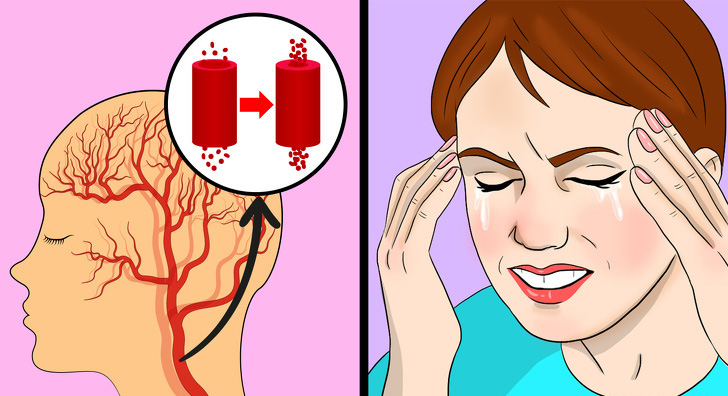
Excessive sodium intake increases the volume of your blood, taking up more space in your blood vessels. This expansion of the blood vessels causes high blood pressure (hypertension) and, as a result, can cause severe headaches.
1. Cognitive Problems
Hypertension caused by high salt intake can damage the arteries that lead to your brain. This can affect your ability to think clearly and make it difficult to concentrate on daily tasks.
Also, constant dehydration can lead to forgetfulness, tiredness, and a slow reaction time.
How To Reduce Your Salt Intake
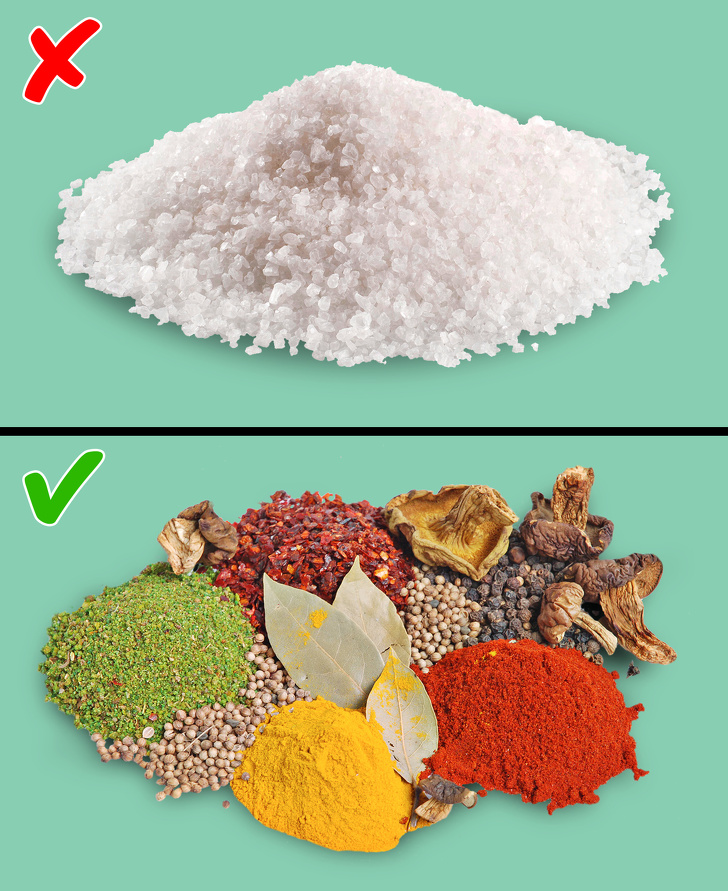

Stay away from “Salty Six” foods:bread and rolls, pizza, sandwiches and burgers, cold cuts and deli meats, canned soups, burritos, and tacos.
Avoid processed or restaurant foods, as they are generally rich not only in additives and preservatives but also in sodium.
Always look at the nutrition label and check the sodium percentage – it is best to choose foods with 5% or less of the daily value of sodium per serving.
Try new flavors! Instead of adding salt, try enhancing the taste of your meals with fresh or dried herbs or acids like lemon juice and vinegar.
How much salt do you eat daily? Tell us about your eating habits in the comments!
Source: crfatsides









