
What is bilberry? It sounds a lot like blueberry, and rightfully so, as it’s a relative to the benefit-rich blueberry and most commonly used to make jams and pies — but did you now it’s also been used for centuries?
Historically, bilberry fruit was used to help treat diarrhea, scurvy and other conditions. Today, the fruit is used as a traditional remedy for diarrhea, eye problems, varicose veins, poor circulation and even cancer prevention.
The bilberry leaf, in addition to the fruit, is used for other conditions, including diabetes. The fruit of the bilberry plant can be eaten just like a blueberry or made into extracts. Similarly, the leaves can be made into extracts or used to make bilberry tea.
What makes this berry so phenomenal is that it contains naturally producing chemicals known as anthocyanosides. Anthocyanosides are plant pigments that have powerful antioxidant properties.
In fact, a study out of the U.K. showed that bilberry had positive effects on vision in lower light environments thanks to its anthocyanosides. These antioxidants scavenge the body for free radicals, with the intention of helping prevent or reverse damaged cells.
Ad

That’s not all bilberry benefits either. Read on to learn more about this powerful fruit.
What Is Bilberry?
The bilberry plant, a low-growing shrub with flowers seen in red, blue and purple colors, is native to Northern Europe and also grows in North America and northern Asia.
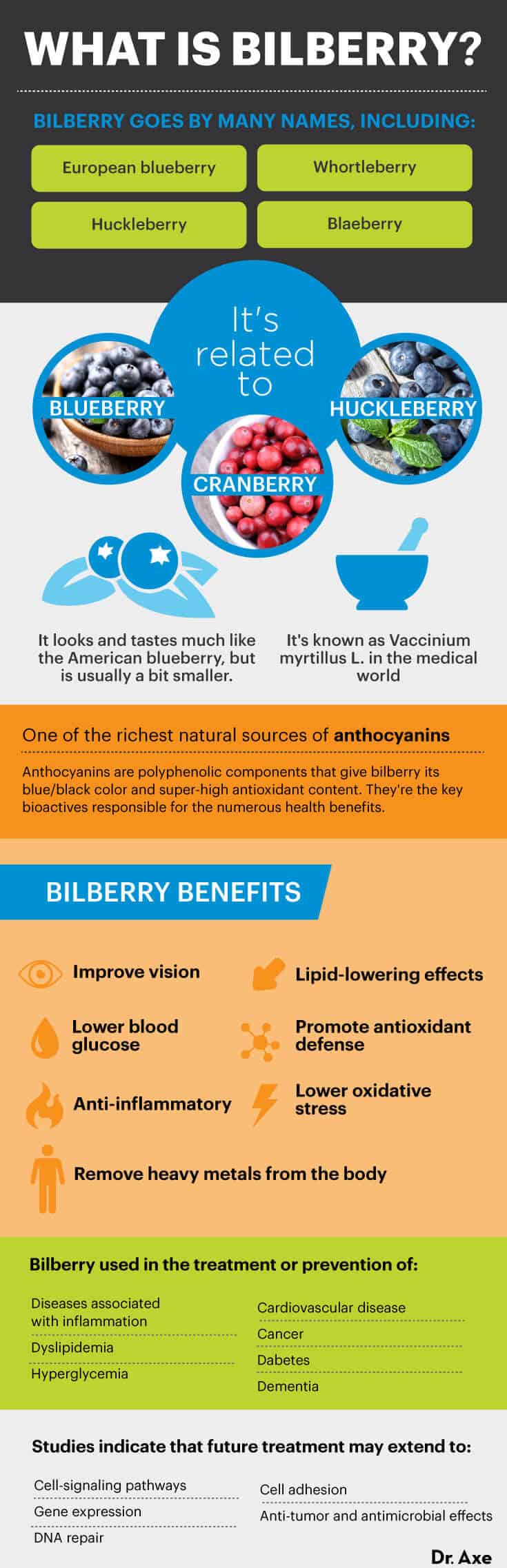
Bilberry is also known as European blueberry, whortleberry, and blaeberry and is a relative of blueberry, cranberry and huckleberry. It looks and tastes much like the American blueberry but is usually a bit smaller, and it is sometimes called blueberry because of their similarities.
This healthy berry usually grows in heaths, meadows and moist coniferous forests, thriving best in moderate shade and moderately humid ground conditions.
It is a small fruit coming in at about five to nine millimeters in diameter, bluish-black in color containing many seeds. The plant is a perennial shrub that grows to about 16 inches in height and has sharp-edged, green branches and black-wrinkled berries that are ripe for picking in late summer.
The usual daily dietary intake of the anthocyanin-producing bilberry is approximately 200 milligrams and has higher anthocyanin content compared to other types of berries, such as strawberry, cranberry, elderberry, sour cherry and raspberry, making it a true superfood! Recommended daily dosages vary greatly depending on the form of bilberry you choose.
Most notably, the bilberry, also know as Vaccinium myrtillus L. in the medical world, is one of the richest natural sources of anthocyanins. Anthocyanins are polyphenolic components that give the berry its blue/black color and super-high antioxidant content.
These powerful anthocyanins are believed to be the key bioactives responsible for the numerous health benefits of bilberry and similar berry fruits. Bilberry is most famous for its ability to improve vision, but it has been reported to help lower blood glucose, have anti-inflammatory and lipid-lowering effects, promote antioxidant defense, and lower oxidative stress.
This makes the fruit highly sought after in the prevention and treatment of diabetes, inflammation, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, increased oxidative stress, cardiovascular disease, cancer and dementia, in addition to other age-related diseases.
Bilberry contains numerous phenolic compounds, including the flavonols, quercetin, catechins, tannins, ellagitannins and phenolic acids. However, the anthocyanins found in the fruit are, by far, the largest contribution to its phytonutrient density. These phenolic compounds are antioxidants as well as iron chelators, which may help remove heavy metals in the body and be used in chelation therapy.
Even though most of the focus is on the antioxidant properties of this fruit, studies have shown that the effects may extend to involve cell-signaling pathways, gene expression, DNA repair and cell adhesion, as well as anti-tumor and antimicrobial effects.
Health Benefits
1. Supports Improved Vision
Due to the anthocyanosides, bilberry is widely used to improve night vision or vision handicaps in low light, decreasing vascular permeability and capillary fragility. It was reported that during World War II, British fighter pilots had improved nighttime vision after eating bilberry jam.
Bilberry has been suggested as a potential treatment for retinopathy, which is damage to the retina. It has also exhibited protective effects against macular degeneration, glaucoma and cataracts, particularly when used with lutein and other eye vitamins.
2. Helps with Circulation Problems
In Europe, health care professionals use bilberry extracts to treat circulation problems, also known as chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). Research suggests that this condition, which occurs when valves in veins in the legs that carry blood to the heart are damaged, may be improved by taking bilberry extract.
READ RELATED: 20 Acai Bowl Recipes — the Superfood Detox Breakfast
Other research suggests that taking bilberry anthocyanins daily for up to six months might improve swelling, pain, bruising and burning associated with CVI.
Ad

3. Can Improve Bad Cholesterol
The amazing anthocyanosides found in bilberries may strengthen blood vessels and prevent the oxidation of LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, a major risk factor for atherosclerosis.
A 2013 study reported that bilberry enrichment, when compared to black currants, reduced total and LDL-cholesterol levels. In fact, the total anthocyanin content was four times higher in bilberries than in black currants, possibly making it a better choice for reducing LDL cholesterol levels.
4. May Improve Blood Sugar Levels
Traditionally, bilberry leaves have been used to control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. Research shows that most berries help reduce the body’s glucose response after eating a high-sugar meal, and studies suggest bilberry may be effective for managing blood sugar levels, particularly when combined with oatmeal, though more research is needed.
It’s also been shown to decrease blood glucose in mice.
5. May Help Prevent Cancer
In vitro work and animal tumorigenic models have demonstrated that the anthocyanins in this fruit have cancer-preventive qualities and suppressive activity due to antioxidants. The berries also have anti-inflammatory effects.
A commercial anthocyanin-rich extract from bilberry was shown to inhibit the growth of colon cancer cells.
6. Effective for Helping with Diarrhea
Bilberry has been used in European medicine to treat diarrhea for many years. The fruit contains tannins, substances that act as both an anti-inflammatory and an astringent that helps with constricting and tightening tissues. By reducing intestinal inflammation, it is believed to help with reducing the symptoms of diarrhea.
7. Helps Lower the Risks of Alzheimer’s Disease
Evidence suggests that fruit and vegetable juices containing various phenolic compounds can reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. In some cases, symptoms of Alzheimer’s were significantly decreased upon treatment with myricetin, quercetin or anthocyanin-rich extracts found in bilberry and showed that behavioral abnormalities may have been alleviated.
How to Add to Diet
Bilberry is typically sold as fresh, frozen or dried whole berries but is often found in the form of preserves, jams and juices. It’s increasingly seen as liquid or powdered concentrates in the supplements section at the grocery as well.
It is found as fresh, dried, a bilberry tea and extracts in both liquid and powder forms. When looking for a bilberry extract, it should contain 25 percent anthocyanidin.
Because of the powerful claims of this fruit, it is no surprise that common marketing tactics are used to make you think a product is filled with bilberry or, more commonly, the extract. Because of this, there are specific standards that have been developed, but regardless, you need to make sure you are getting the real thing.
Many manufacturers include various berry types, and this predominantly occurs with anthocyanin-rich extracts from other species, such as bog bilberry, lingonberry, European elder and Chinese mulberry. It has even been reported that black soybean hull or black rice extracts have been used as well as synthetic colorants, like amaranth dye, an azo dye that has been prohibited for use by the FDA as a suspected carcinogen. Always read labels carefully.
Once you certify the veracity and quality, you can add bilberry in your diet in many ways. For instance:
- Brew into tea
- Add to muffins
- Mash the berries as a spread or make bilberry jam
- Put on top of yogurt, granola, oatmeal, etc.
- Toss them in a smoothie
- Put them in salads
- Use as a pancake topping
- Juice them
- Make bilberry pie
- Or just use them in place of blueberries in just about any recipe
In addition, you can make a bruise cream with arnica and bilberry.
Risks, Side Effects and Drug Interactions
Bilberry fruit and extract are considered generally safe, with no known side effects, but it is important to be aware of possible side effects. Because the anthocyanosides in this fruit may stop blood from clotting, there may be an increased risk of bleeding if you take bilberry with blood-thinning medication, which includes aspirin.
The whole fruit may be safer than concentrated forms. Ask your doctor before taking bilberry, especially if you take blood-thinning medication or are diabetic, pregnant or breastfeeding.
Long-term safety and side effects have not been extensively studied, and high doses or extended use of bilberry leaf or leaf extract may be unsafe due to possible toxic side effects.
Final Thoughts
- Bilberry is a fruit that’s a relative to the benefit-rich blueberry and is most commonly used to make jams and pies.
- Historically, the fruit was used to treat diarrhea, scurvy and other conditions. Today, it is used as a potential remedy for diarrhea, eye problems, varicose veins, poor circulation and even cancer prevention.
- There are many ways to utilize this fruit, so try it today for a burst of health-promoting compounds and a delicious flavor.
!function(f,b,e,v,n,t,s)
{if(f.fbq)return;n=f.fbq=function(){n.callMethod?
n.callMethod.apply(n,arguments):n.queue.push(arguments)};
if(!f._fbq)f._fbq=n;n.push=n;n.loaded=!0;n.version=’2.0′;
n.queue=[];t=b.createElement(e);t.async=!0;
t.src=v;s=b.getElementsByTagName(e)[0];
s.parentNode.insertBefore(t,s)}(window, document,’script’,
‘
fbq(‘init’, ‘3475171552810057’);
fbq(‘track’, ‘PageView’);



