![]() VERIFIED
VERIFIED
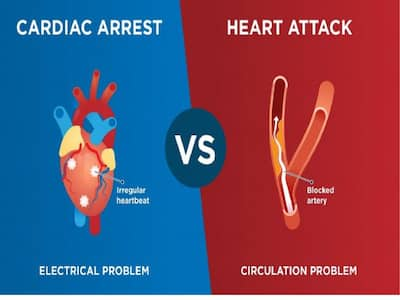
Both sudden cardiac arrest and heart attacks are heart-related emergencies that can be lethal. To learn how they differ from one another, scroll down.
Heart attack and sudden cardiac arrest are two different medical conditions which are often confused to be the same. Heart attack is a condition characterized by blockage of blood flow to the heart. Sudden cardiac arrest is a condition in which the heart suddenly malfunctions and stops beating. In other words, a heart attack is a problem with blood circulation while cardiac arrest is an electrical problem.
On World Heart Day, we spoke to Dr. Amit Bhushan Sharma, Director and Unit head of Cardiology, Paras Health, Gurugram, to understand how to differentiate between a heart attack and a cardiac arrest. Scroll down to know everything about the two dangerous heart conditions and their unique symptoms.
Heart Attack vs. Sudden Cardiac Arrest: How to Tell the Difference and What to Do
A heart attack occurs when one of the coronary arteries gets blocked and prevents the supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart. As a result, the part of the heart that is not receiving oxygen starts to die. The longer the artery remains blocked, the greater the damage. The blockage can be caused due to blood clots or plaque build-up which leads to the thickening of the walls of arteries due to cholesterol deposits.
Symptoms of Heart Attack
The symptoms of a heart attack may be mild to immediate and intense. Some common symptoms of heart attack include:
- Chest pain
- Tightness of the chest
- Spreading of pain to other body parts such as arms, jaw, neck, back, and abdomen
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Coughing
- Anxiety
- Restlessness
- Dizziness
- Sweating
- Weakness, and
- Palpitations
The symptoms of a heart attack can even be different for men and women. If someone experiences any of these symptoms, immediate medical attention must be crucially provided. The treatment of a blocked artery includes medications to dissolve the clot, angioplasty, and the placement of stents to keep the artery open.
What Is A Sudden Cardiac Arrest?
Sudden cardiac arrest is the sudden loss of heart activity due to a malfunction. As a result, the heart stops beating and breathing stops. Without treatment, cardiac arrest can even lead to the death of a person. However, as a first aid, hands-only CPR can significantly enhance the chances of survival during a cardiac arrest.
READ RELATED: Painful Ingrown Nails? Try These Natural Techniques For Fast Relief
Furthermore, an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) also increases the chance of survival for someone under cardiac arrest while the person waits for professional medical help. Sudden cardiac arrest can be caused by to heart attack, a severe hemorrhage, a severe drop in oxygen levels, electrocution, a drug overdose, choking, hypothermia, excessive alcohol consumption, heart disease, and many others. Some common symptoms of cardiac arrest include collapse, no pulse, no breathing, loss of consciousness, discomfort in the chest, shortness of breath, weakness, and palpitations in some cases.
Heart Attack vs. Sudden Cardiac Arrest: What to Do If You Experience These Dangerous Symptoms
Both heart attack and cardiac arrest require immediate medical attention. If someone experiences any of the symptoms of heart attack or cardiac arrest, they should be urgently provided the first aid and professional medical help should not be delayed. Quick actions can significantly improve the condition of the patient and improve the chances of treatment and even survival. In addition, one must make certain changes in their lifestyle to live a better life free of heart disease. Simple lifestyle changes such as healthy food, regular exercise, avoiding any kind of drugs and various others can prove to be significantly helpful in improving the overall health of a person.
Total Wellness is now just a click away.
Follow us on
Don’t Miss Out on the Latest Updates.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter Today!
window.addEventListener(‘load’, (event) => {
$(‘#commentbtn’).on(“click”,function(){
(function(d, s, id) { var js, fjs = d.getElementsByTagName(s)[0]; if (d.getElementById(id)) return; js = d.createElement(s); js.id = id; js.src = “//connect.facebook.net/en_US/sdk.js#xfbml=1&version=v2.3”; fjs.parentNode.insertBefore(js, fjs);}(document, ‘script’, ‘facebook-jssdk’));
$(“.cmntbox”).toggle();
});
});










