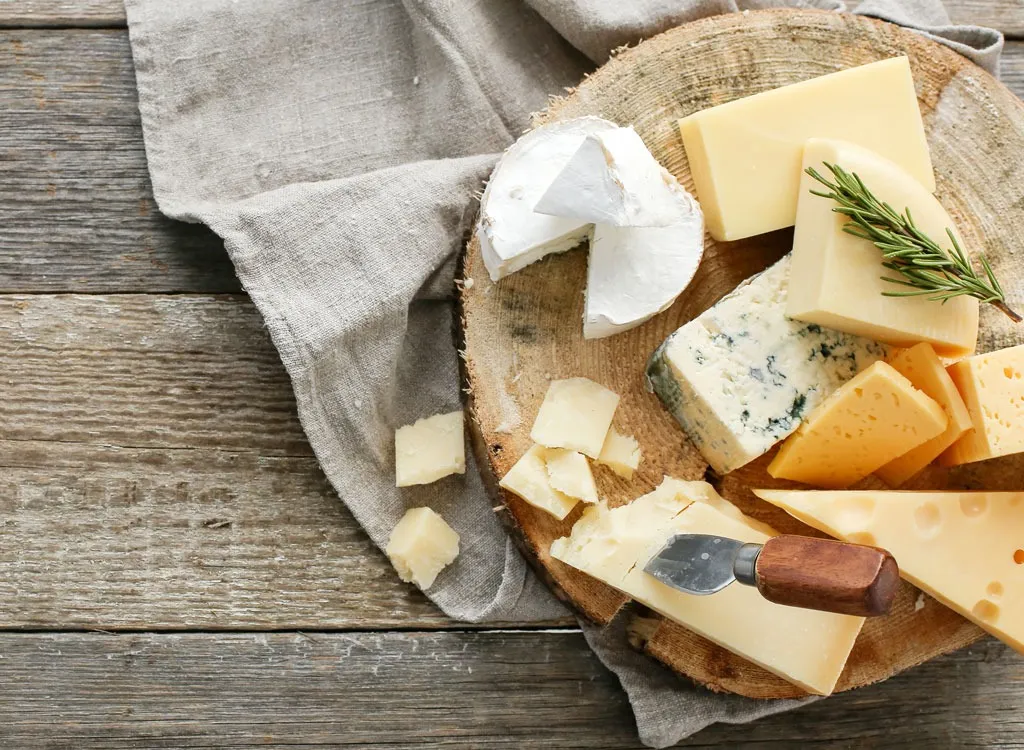
Finding a balance between flavor and health is a challenge for cheese lovers who are watching their sodium intake. While cheese contains essential nutrients like calcium and protein, it’s also a significant source of sodium, which can contribute to high blood pressure and other health problems when eaten in excess.
However, as low-sodium cheeses are available, you don’t have to give up your favorite food entirely to keep your sodium levels in check. According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, food is low in sodium when it contains 140 milligrams or less per serving. You can maintain a balanced diet without sacrificing flavor by choosing low-sodium cheeses more often.
Read on to learn about six of our favorite low-sodium cheeses that allow you to enjoy cheese without compromising your health. Plus, learn how to include them in a healthy eating plan.
Why Sodium Content in Cheese Matters
While sodium is an essential mineral that helps regulate fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions, eating too much sodium can lead to health problems like high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
The American Heart Association recommends limiting sodium intake to no more than 2,300 milligrams daily. For those with high blood pressure or heart concerns, an ideal sodium limit is 1,500 milligrams per day.
Cheese can be a significant source of sodium in your diet, with some varieties, such as Parmesan, containing more than 300 milligrams of sodium per 1-ounce serving. If you’re a cheese lover trying to reduce sodium intake, choosing low-sodium options is important.
6 Low-Sodium Cheeses
Fortunately for cheese lovers, several low-sodium cheeses are available. Here are six of our favorites.
Mascarpone
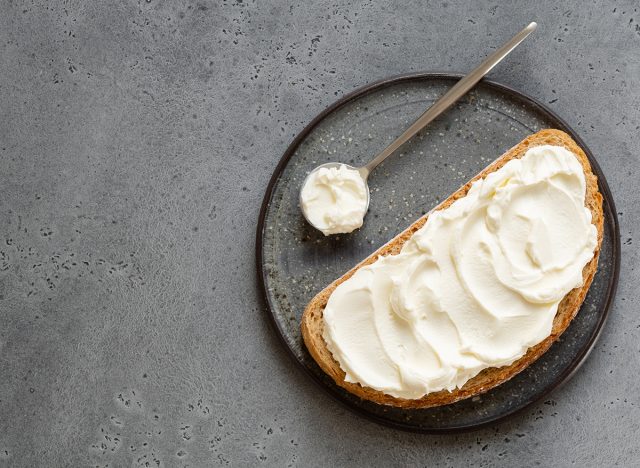

Sodium (per 1 oz): 14 mg
Mascarpone is a rich, creamy, and slightly sweet cheese made from whole cream. It works well in desserts but can also be used in savory dishes like risotto or as a spread. It can also be stirred into pasta sauce with mushrooms and spinach to create a creamy sauce.
Ricotta
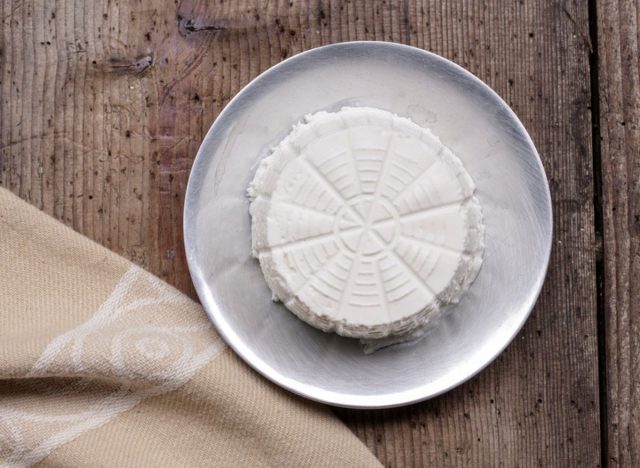

Sodium (per 1 oz): 28 mg
Ricotta cheese is a creamy, mild cheese often used in Italian cuisine. It’s naturally low in sodium and high in calcium, making it a nutritious choice for those watching their sodium intake. Add it to pasta dishes like lasagna or stuffed shells, or mix it into pancake batter for a richer, fluffier texture.
Swiss
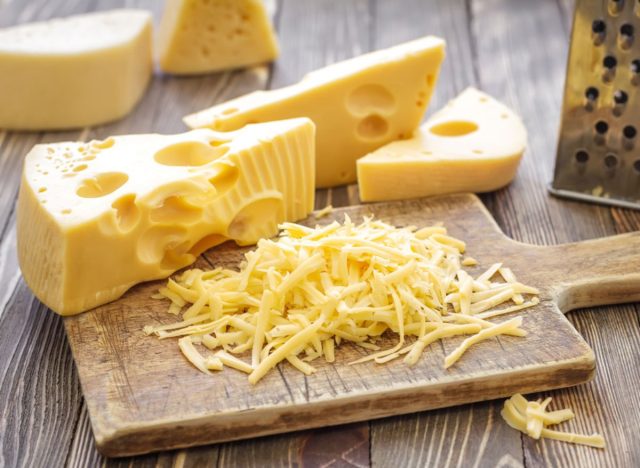

Sodium (per 1 oz): 53 mg
Swiss cheese is a popular low-sodium cheese thanks to its distinctive nutty flavor and firm texture. Use it to make a classic grilled cheese sandwich on whole wheat bread or incorporate it into an omelet with spinach and mushrooms for a savory, protein-packed breakfast.
Cream Cheese
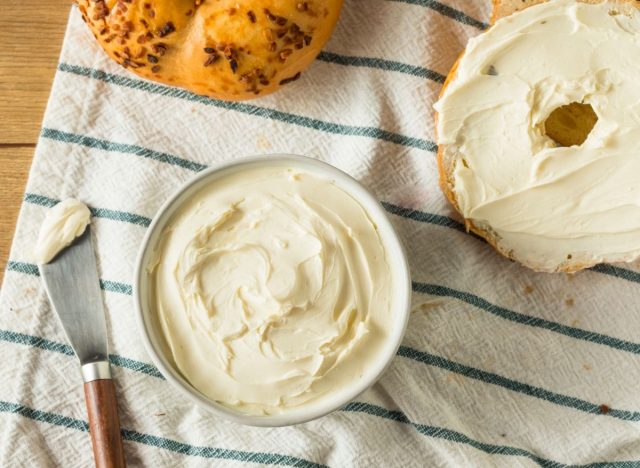

Sodium (per 1 oz): 89 mg
While some cream cheese is high in fat, it’s low in sodium compared to many other cheeses. For an even healthier choice, opt for a lower-fat version. Blend it with plain Greek yogurt, lemon juice, and garlic for a lighter protein-packed dip, or add a small amount to marinara sauce to add creaminess without relying on heavy cream.
Soft Goat Cheese
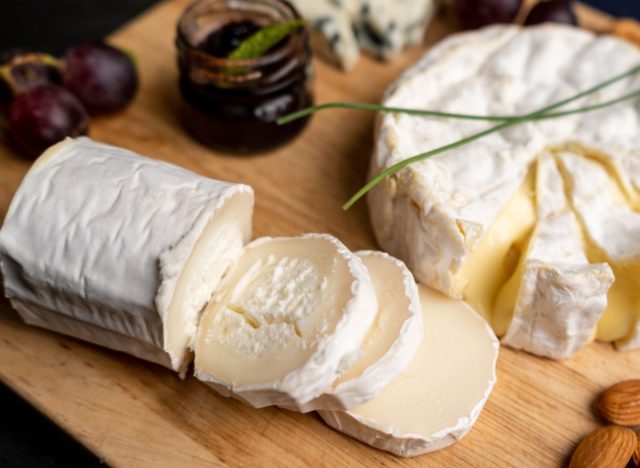

Sodium (per 1 oz): 130 mg
Soft goat cheese is lower in sodium than many cows’ milk cheeses, and its tangy flavor pairs well with a variety of dishes. A bonus? It’s lower in lactose than cow’s milk cheese, which makes it easier for people with lactose intolerance to digest. For a tangy and sweet lunch, try crumbled goat cheese over a salad with roasted beets, orange slices, and mixed greens.
Mozzarella
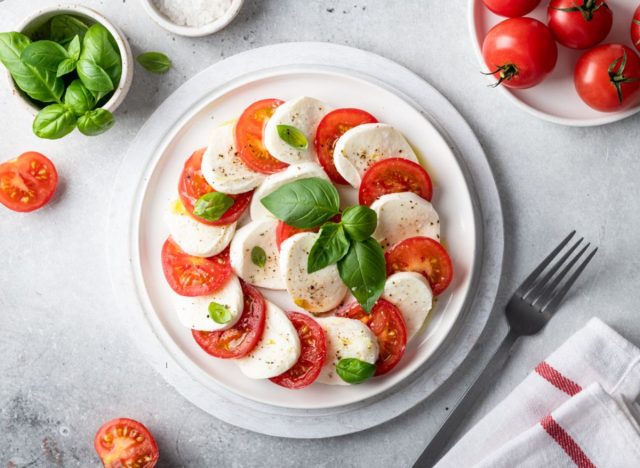

Sodium (per 1 oz): 138 mg
Mozzarella cheese‘s mild flavor and soft texture make it a versatile low-sodium cheese that can be added to various dishes. Layer fresh mozzarella slices with ripe tomatoes and fresh basil drizzled with balsamic vinegar and olive oil, or toss baby spinach with fresh strawberries, nuts, and small mozzarella balls (bocconcini) for refreshing and nutrient-packed salads.
Tips for Incorporating Low-Sodium Cheeses Into Your Diet
There are many flavorful ways to incorporate low-sodium cheeses into your diet, from using cheese as a flavor enhancer to pairing low-sodium cheese with whole foods to create balanced meals and snacks.
Use Cheese as a Flavor Enhancer
Instead of relying on large portions of cheese, use small amounts of low-sodium cheese to add flavor to your meals. For example, add a few slices of fresh mozzarella to your salads or replace higher-sodium cheddar cheese with Swiss cheese in sandwiches or wraps.
Pair With Whole Foods
Combine low-sodium cheeses with fresh, whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to create balanced, nutrient-dense meals. For example, pair ricotta cheese with fresh pineapple or cherry tomatoes for a nutritious snack, or top a slice of whole wheat bread with low-fat cream cheese, avocado, and an egg for a tasty and filling breakfast.
Experiment with Different Types of Low-Sodium Cheeses
Many low-sodium cheeses are softer cheeses. Experiment with different ways of adding them to your meals to find the ones that best suit your flavor preferences and dietary needs.
If you enjoy cream cheese, mix it with herbs and spices to create a flavorful spread for whole wheat crackers or raw veggie sticks. If you often use heavy cream in recipes, try adding low-fat cream cheese instead, which adds creaminess without added fat.
Conclusion
Reducing your sodium intake doesn’t have to mean giving up your favorite foods, such as cheese. By choosing low-sodium options, such as ricotta, Swiss, mascarpone, cream cheese, soft goat cheese, or mozzarella, you can continue to enjoy the rich, creamy flavors and nutritional benefits without completely eliminating cheese from your diet.
Instead of making cheese the main focus of your meal, use it to enhance its flavor. This will help you stick to a 1-ounce serving size and keep your sodium intake low. By experimenting with different types of cheese and incorporating them into whole-food-based meals, you can follow a low-sodium diet without sacrificing flavor.