Collagen is the most abundant protein in our bodies, and that’s because it’s vital to many aspects of our health. Unfortunately, there are many things that can decrease our collagen levels, which is why supplementing with something like bovine collagen is a good idea.
First of all, we naturally start to lose collagen as we age, but we can also lose collagen due to:
- hormonal changes
- drugs
- alcohol
- processed foods
- white sugar
- hydrogenated oils
- overwork
- radiation
- fluoridated water
- excess sun
- nutritional deficits
- dehydration
- stress
- trauma
This is why it’s important to supplement with outside collagen sources as well, like bovine collagen.
While collagen sources in food exist, it can be hard to consume the parts of the animals where the collagen is concentrated.
One way to obtain bovine collagen from food sources is by making homemade bone broth. The benefits of bone broth are truly awesome so this is a great option.
Another smart and convenient choice is the use of collagen supplements.
Since it delivers a dense collagen punch to your cells, a bovine collagen supplement is one of the most beneficial and straightforward ways to up your collagen intake. When you use high-quality, hydrolyzed collagen supplements, the protein breakdown is already halfway there, so to speak, because the usable small chain peptides and amino acids are ready to go — your body just has to put them to work for you.
So what exactly does that mean, what is bovine collagen and why should you make sure to add it to your health regimen? Let’s find out.
What Is Bovine Collagen?
Bovine collagen is also known as bovine cartilage or beef collagen. Gelatin is a form of hydrolyzed beef collagen, which means it’s essentially a part of broken-down collagen.
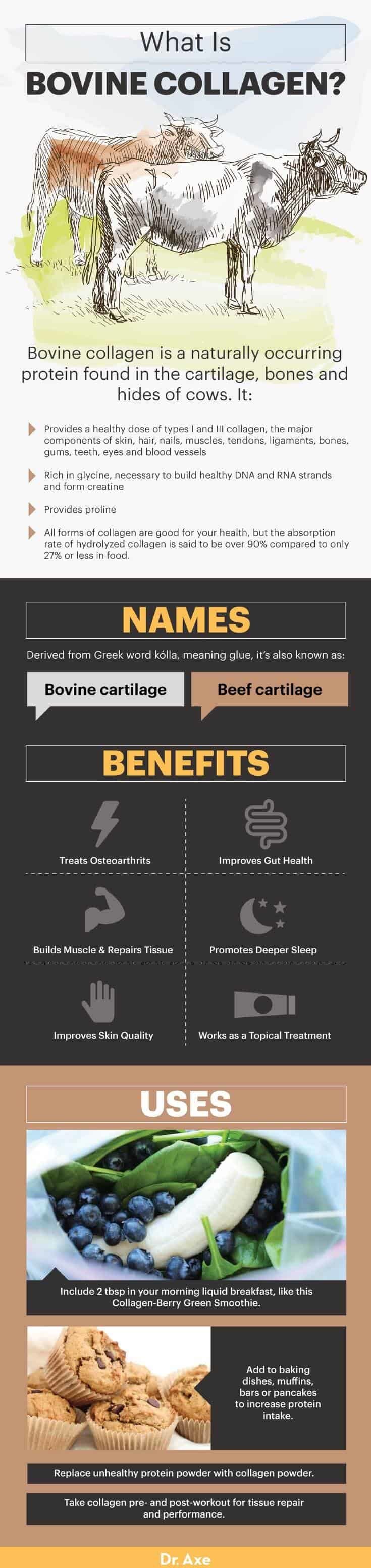
Where does bovine collagen come from? It’s a naturally occurring protein found in the cartilage, bones and hides of cows. This type of collagen is very similar to what we have in our bodies and provides a healthy dose of types I and III collagen.
Type I collagen and type III collagen are the major components of skin, hair, nails, muscles, tendons, ligaments, bones, gums, teeth, eyes and blood vessels. Together, types I and III collagen make up more than 90 percent of the collagen in our bodies.
Bovine collagen is rich in the amino acid glycine, which is necessary for building healthy DNA and RNA strands. These are the essential genetic building blocks for properly functioning body cells.
Glycine is also one of the three amino acids that form creatine. Creatine is known to promote healthy muscle growth and aid in energy production during workouts.
Last but not least, bovine collagen also provides the amino acid proline. Proline plays a critical role in the body’s ability to produce its own collagen.
Hydrolyzed beef collagen was produced as a food supplement after scientists learned to break the long chain triple helix protein into shorter pieces and then separate the three helices from each other. The resulting short individual peptides make up hydrolyzed collagen.
Related: Beef Gelatin: What Are the Benefits & How Does It Compare to Collagen?
Benefits
1. Helps Treat Osteoarthritis
Research continues on collagen’s value in treating bone and joint diseases like arthritis, but there is growing evidence that collagen hydrolysate might be able to help patients with osteoarthritis (OA).
When you have OA, it causes joint cartilage to become stiff and lose its flexibility. This decline in joint health makes a sufferer even more susceptible to joint damage.
Over time, this degenerative joint disease can cause cartilage to wear away, leading to pain, and eventually the bones could even rub against each other.
Multiple studies have shown collagen hydrolysate to be safe and to provide improvement in some measures of pain and function in men and women with OA or other arthritic conditions. Since cartilage is made up of collagen, it makes sense that supplementing with this building block could help the strength and framework of the cartilage itself.
Collagen hydrolysate (which is the same thing as hydrolyzed collagen) is of interest as a potential medical treatment for osteoporosis as well. Some researchers believe its high level of safety makes it an excellent long-term treatment for osteoarthritis and osteoporosis, which are both chronic disorders.
If you suffer from either condition, you should include bovine collagen as part of your arthritis diet and/or osteoporosis diet treatment plan.
2. Can Improve Gut Health
Collagen contains vital amino acids, which have been shown to be beneficial to the entire gastrointestinal system. That includes the stomach as well as the intestines.
Studies show that one of these amino acids, glycine, actually improves digestion by increasing gastric or stomach acid. This acid is an essential digestive liquid produced in the stomach.
Through the use of collagen to increase low stomach acid levels, you’re able to better digest your food, which can prevent and help troubling heartburn and gastroesophageal reflux disease. It can also help leaky gut syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease, which also tend to involve low stomach acid.
Research indicates that glycine is also helpful with detoxification, which is excellent for your digestive health as well as your overall health. Glycine is actually one of the precursor amino acids to glutathione, a major antioxidant and detoxifying agent in the body.
3. Builds Muscle and Repairs Tissue
Beef collagen is a structural protein found in cows so it’s inherently a super-high protein source. More specifically, beef collagen contains types I and III collagen, which are the best types of collagen to consume when it comes to workout and muscle recovery.
Collagen types I and III specifically support the tendons and ligaments that you use every time you exercise. By consuming collagen pre- and post-workout, you can help your body recover better and faster from physical exertion of all kinds.
Bovine pericardium also is used extensively in medical applications, including bio-prosthetic heart valves, dural closure, bone and dental membranes, and surgical buttressing. Because it’s mostly collagen, bovine pericardium is both strong and elastic.
In fact, lyophilized bovine collagen matrix has even been used in postoperative wound healing. One pilot study found that “type I bovine collagen matrix provided a safe, readily available alternative to traditional methods of second intention healing.”
However, another study concluded that using porcine collagen (from a pig) does not appear as safe, according to the research.
4. Promotes Deeper Sleep
The most abundant amino acid in collagen is glycine, an immunonutrient that supports healthy inflammation response and also promotes deeper, more restorative sleep. Human and animal studies have shown that glycine affects neurotransmitters in a way that promotes better quality sleep, making bovine collagen a natural sleep aid.
In animals, findings show that oral administration of glycine increases extracellular serotonin release in the prefrontal cortex. The results of three human trials demonstrate that glycine improves sleep quality in a subjective and objective manner with no serious adverse effects.
5. Improves Skin Quality
When taken internally, collagen can really improve the overall health of your skin, making for an excellent natural skin care product. It helps form elastin and other compounds within skin that are responsible for maintaining skin’s youthful tone, texture and appearance.
Collagen is accredited with helping reduce the visible signs of wrinkles, decreasing puffiness and fighting various other signs of aging.
READ RELATED: Parkinson’s disease: The signs in your vision people 'often experience' – symptoms
Many people report a decrease in cellulite when consuming foods and supplements containing collagen, since cellulite forms due to a lack of connective tissue, allowing skin to lose its firm tone.
A double-blind, placebo-controlled study investigating the anti-aging properties of collagen conducted by the University of Kiel’s Department of Dermatology found that 2.5—5 grams of collagen hydrolysate used among women aged 35–55 once daily for eight weeks supports skin elasticity, skin moisture, transepidermal water loss (dryness) and skin roughness.
At the end of only four weeks, those using collagen showed a statistically significant improvement in comparison to those using a placebo with regard to skin moisture and skin evaporation, plus noticeable decreases in signs of accelerated aging.
6. Works as a Topical Treatment
Bovine collagen is also typically used to help with several common issues. One study suggests that a topical ointment and bovine type I collagen spray are effective in the treatment of acute anal fissures (or small tears) in children.
For itchiness near the anus (anal pruritus), a cream with 5 percent bovine collagen applied two or more times daily can offer relief. Beef collagen might also help reduce symptoms of hemorrhoids when applied externally on the rectum.
A facial cream that includes bovine collagen can also help improve acne. Apply the cream twice a day to clean skin.
Are your gums sore after having a tooth pulled? It sounds strange, but people have found relief from beef collagen.
Simply combine a powdered bovine collagen with salt water to form a paste, and pack it into the dry socket after a tooth extraction.
Types and Supplements
With the rising popularity of collagen supplements, there are many varieties of powders, capsules and drinks on the market. So how you know what type of collagen is best for you?
Although humans naturally produce collagen, production decreases with age. This can lead to skin aging and changes with muscle and joint health.
Collagen supplements are derived from a number of sources, with bovine collagen (specifically from cows) the most popular. Other forms include marine collagen and collagen from eggshell membranes.
While bovine collagen features types I and III collagen, marine collagen offers types I and II. This is why using a multi-collagen complex that features several sources is ideal.
Another important factor to consider when you’re shopping for collagen supplements is digestibility/absorption. When you consume collagen through foods and supplements, as either marine collagen or one derived from cows or egg shells, your body has to be able to break down and properly utilize this complex protein.
The digestive system has to go to work breaking the collagen down into simpler, more usable forms of peptides and amino acids. Then, these smaller molecules get absorbed in the small intestine into the blood. Finally, these molecules go to all of the many places they’re needed and get reassembled into collagen.
Sounds like quite the process, right? Additionally, digestion of dietary collagen can often be incomplete and result in very large peptide chains, which are not well-utilized by the body.
There is a way to make it easier, and it’s to make sure that you purchase a collagen supplement that is already hydrolyzed. This means that the collagen has already been broken down into more easily digestible and usable forms.
I highly recommend a bovine hydrolyzed collagen supplement in powdered form. This collagen powder is a light yellow to off-white color.
It’s easy to add the collagen to smoothies and other drinks, as well as soups, stews and baked goods. Compared to gelatin, which has long chains of amino acids, hydrolyzed collagen has shorter chains of amino acids that are more easily digested.
In case you’re getting confused, gelatin is the cooked form of collagen that’s in the foods you eat (think the childhood favorite jello).
Related: Fish Collagen: The Anti-Aging Protein with the Best Bioavailability
Nutrition
This is an example of the nutritional content found in two scoops (20 grams) of a high-quality, grass-fed bovine collagen supplement:
- 72 calories
- 18 grams protein
- 108 milligrams sodium
A serving a bovine collagen contains the following amino acids:
- 1,462 milligrams alanine
- 1,517 milligrams arginine
- 1,192 milligrams aspartic acid
- 2,239 milligrams glutamic acid
- 3,719 milligrams glycine
- 144 milligrams histidine*
- 217 milligrams hydroxylysine
- 2,058 milligrams hydroxyproline
- 271 milligrams isoleucine
- 524 milligrams leucine*
- 614 milligrams lysine*
- 108 milligrams methionine*
- 379 milligrams phenylalanine*
- 2,076 milligrams proline
- 614 milligrams serine
- 342 milligrams threonine*
- 90 milligrams tyrosine
- 433 milligrams valine*
How to Use (Recipes)
Bovine collagen supplements come in three different forms:
- Real foods like bone broths
- Gelatin
- Hydrolyzed collagen supplements
All forms of collagen are good for your health, but the absorption rate of hydrolyzed collagen is said to be over 90 percent compared to only 27 percent or less in food.
If you’re looking to get your collagen from major food sources, then you definitely want to start consuming bone broth. Check out my recipe for making homemade Beef Bone Broth.
As this delicious and nutritious liquid simmers, the natural collagen in the beef bones leaches into the broth. When you’re really short on time, always make sure to buy a high-quality bone broth that’s ideally organic and made from grass-fed beef bones.
Once you’ve selected the right product for you, it’s time to explore bringing it into your diet. Here are some of the easiest ways to use a bovine collagen powder:
- Include two tablespoons in your morning liquid breakfast, like this Collagen-Berry Green Smoothie.
- Add to baking dishes, muffins, bars or pancakes to increase protein intake.
- Replace unhealthy protein powder with collagen powder.
- Take collagen pre- and post-workout for tissue repair and performance.
Follow dosing instructions on the particular product you use, or consult a health care expert if you are unsure of appropriate dosage. Always store collagen products in a cool, dry place.
Risks and Side Effects
Hydrolyzed bovine collagen is widely used in nutrition supplements. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration considers it as generally recognized as safe. It’s also a widely accepted and considered a safe food additive in many countries.
Bovine cartilage is considered safe when taken in proper amounts by mouth or applied to the skin. Generally, it does not tend to cause any significant side effects.
Minor side effects, however, can include digestive upset or rash. If you have a reaction to topical application of collagen, discontinue use.
Hydrolyzed collagen has not been found to have any significant drug or food interactions, but talk to your doctor before taking collagen if you currently take any other medications.
When it comes to bovine collagen, some people are concerned about mad cow disease, which is a rare illness you can get from eating infected beef. Mad cow disease does not appear to be transmitted through cartilage products like collagen supplements, but it’s probably a good idea to stay away from animal products from countries where mad cow disease has been found.
If you’re pregnant or breast-feeding, collagen supplements are not recommended.
Conclusion
- Collagen is the most abundant protein in our bodies, but we naturally start to lose collagen as we age. We can also lose collagen due to hormonal changes, drugs, alcohol, processed foods, white sugar, hydrogenated oils, overwork, radiation, fluoridated water, excess sun, nutritional deficits, dehydration, stress and trauma.
- Bovine collagen is a naturally occurring protein found in the cartilage, bones and hides of cows that provides types I and III collagen, the major components of skin, hair, nails, muscles, tendons, ligaments, bones, gums, teeth, eyes and blood vessels.
- It’s been shown to help treat osteoarthritis, improve gut health, build muscle, repair tissue, promote deeper sleep, improve skin quality and work as a topical treatment.
- All forms of collagen are good for your health, but the absorption rate of hydrolyzed collagen is said to be over 90 percent compared to only 27 percent or less in food.
Source: