For years we have been told to lather on sun cream and avoid tanning to protect our skin from cancer.
But influencers on social media are not only urging people to ditch sunscreen for a health boost some are even suggesting intentionally burning your skin to ‘heal acne’.
However, dermatologists warn that although there are proven health benefits to getting enough sunlight, sunscreen doesn’t block this and getting sunburnt increases your lifetime risk of skin cancer.
They also stress that there are ‘safer ways’ of clearing acne than burning your skin.
Getting sunburnt, or even just tanned, damages the DNA and causes the death of skin cells which can increase signs of skin aging.
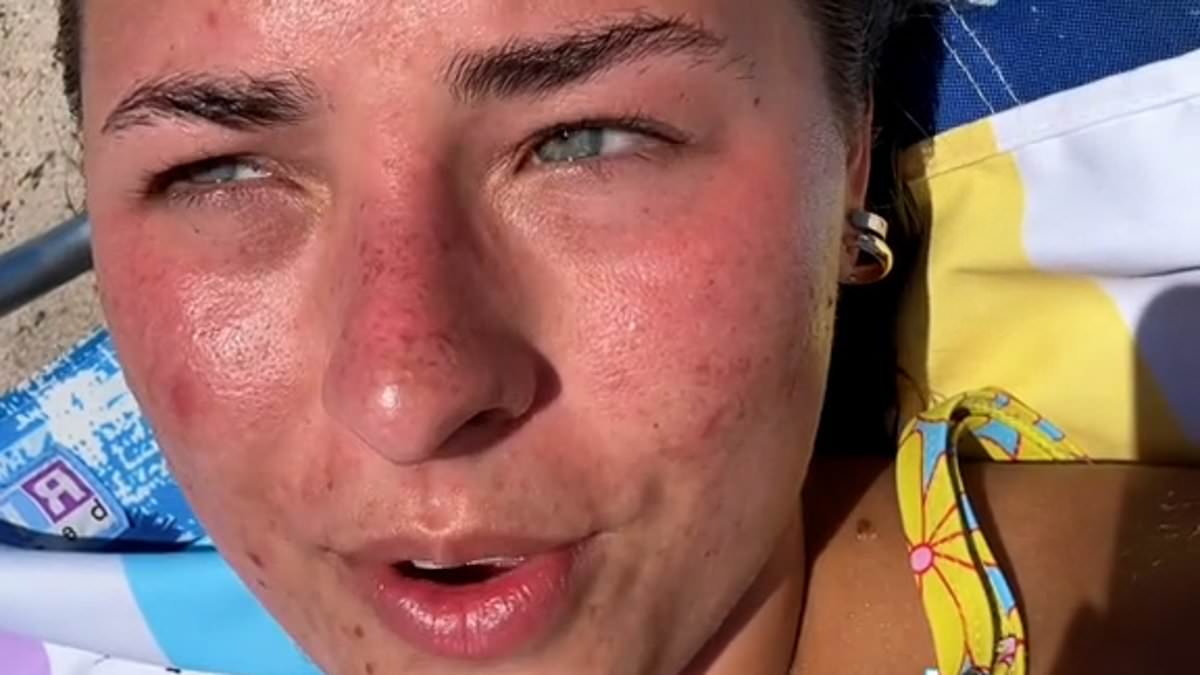
![Social media user @melissanelosn, who has 450K followers, posted a video to TikTok showing her sunbathing on the beach claiming the 'sun and saltwater' 'burns off all [her] acne'](https://i.dailymail.co.uk/1s/2024/08/02/11/88041609-13689291-Social_media_user_melissanelosn_who_has_450K_followers_posted_a_-m-1_1722593120926.jpg)
Social media user @melissanelosn, who has 450K followers, posted a video to TikTok showing her sunbathing on the beach claiming the ‘sun and saltwater’ ‘burns off all [her] acne’
The British Association of Dermatologists advises that people with white skin should wear at least an SPF 30 sunscreen between March and October in the UK to reduce their risk of sunburn and skin cancer.
That’s because sunburn is associated with an increased risk of skin cancers, warns Dr Zainab Laftah, consultant dermatologist and British Skin Foundation spokesperson.
He stressed that this risk doubles in those who have had more than five episodes of sunburn in their lifetime.
However, some social media users are burning their skin in hopes of curing their acne.
Social media user @melissanelosn, who has 450K followers, posted a video to TikTok showing her sunbathing on the beach claiming the ‘sun and saltwater’ ‘burns off all [her] acne’.
In another video captioned ‘benefits of sunbeds’, TikTok user @meghanbrodie claimed sunbeds ‘help with acne and acne scarring’.
She told her 2,997 followers: ‘UV light can help reduce redness, swelling and soreness of breakouts.’

In a video captioned ‘benefits of sunbeds’, @meghanbrodie claimed sunbeds ‘help with acne and acne scarring’

Dr Whitney Bowe, a dermatologist based in the US, reacted to a video on TikTok claiming that sunburn ‘clears’ acne. she warned it can instead cause premature aging and cancer
Dr Whitney Bowe, a US-based dermatologist, is one expert seeking to put these claims into context.
Reacting to a video on TikTok claiming that sunburn ‘clears’ acne, she warned UV rays also increase the risk of skin cancer.
‘Blue light and red light from the sun can actually make acne better, the problem is it comes along with ultra violet rays which can prematurely age the skin and lead to skin cancer,’ she warned.
Dr Justine Kluck, a London-based consultant dermatologist, also told MailOnline there are far safer ways to get rid of spots than risking skin cancer, and the supposed benefits of the sun might actually be down to people feeling less stressed.
‘There are safer ways to treat acne and other skin conditions like psoriasis, than to go out and expose your skin to the sun without the right protection,’ she said.
‘People often report that their skin is better in the sun, especially with acne and other skin conditions like psoriasis as well. To an extent it can have some anti-inflammatory impact on our skin.
‘But we also know that when people are on holiday and out in the sun and not at work, people’s stress levels tend to be lower and that’s good for your skin health.
‘It’s very difficult to measure how much sun and UV you are exposing your skin to without creating damage.’
UV rays can penetrate the first two layers of skin — the epidermis and dermis — and damage cells’ DNA.
Damage in the top epidermis layer causes the body to produce melanin, as part of its attempt to block the sun from continuing its assault.
This usually results in the body tanning, as the substance produces a darker pigment in the skin.
UV is actually made of different waves UVA, which have a longer wavelength and penetrate deeper than to the other form, UVB, which leads to damage in the middle dermis layer over time.
Wearing sunscreen with at least an SFP 30 will help protect your skin from UVB rays. The NHS also advises to buy a sunscreen with at least a four star UVA protection.

Social media user @captain_taylor_morgan, who has more than 322K followers on TikTok , boasted about ‘never wearing sunglasses or sunscreen’
![In one Instagram story, posted by influencer Lauyrn Goodman, she told her near 200,000 followers 'you're brought up to wear sun cream [to] protect yourself', but 'everything you think you know isn't correct'. Instead 'training your skin is key', the 33-year-old who has two children with the married England footballer Kyle Walker, said](https://i.dailymail.co.uk/1s/2024/07/30/17/84954017-13689291-In_one_Instagram_story_posted_by_influencer_Lauyrn_Goodman_she_t-a-7_1722357835877.jpg)
In one Instagram story, posted by influencer Lauyrn Goodman, she told her near 200,000 followers ‘you’re brought up to wear sun cream [to] protect yourself’, but ‘everything you think you know isn’t correct’. Instead ‘training your skin is key’, the 33-year-old who has two children with the married England footballer Kyle Walker, said
But advice from influencers on social media urges people to forgo sunscreen and, incorrectly, claims that doing so will help give your immune system a boost.
Social media user @captain_taylor_morgan, who has more than 322K followers on TikTok, boasts about ‘never wearing sunglasses or sunscreen’.
‘If you use sunscreen you are literally blocking yourself from the most important aspect of health, and that is light exposure,’ he said.
‘We need UV light for vitamin D production.
‘If you are deficient in vitamin D that means your immune system is weakened,’ he added.
In one Instagram story, posted by influencer Lauyrn Goodman, she told her followers ‘you’re brought up to wear sun cream [to] protect yourself’, but ‘everything you think you know isn’t correct’.
Instead ‘training your skin is key’, the 33-year-old who has two children with the married England footballer Kyle Walker, said.
She added: ‘It’s about building up your melanin to handle the sun as well slowly.’
Vitamin D is admittedly important to health, helping regulate the amount of calcium and phosphate in the body.
These nutrients in turn keep bones, teeth and muscles healthy, the NHS explains.
Vitamin D is also necessary for the proper functioning of your immune system — which is your body’s first line of defense against infection and disease.
Most people can make all the vitamin D they need through sunlight on their skin and a balanced diet.
Food such as oily fish, red meat, egg yolks and fortified breakfast cereals are all good sources of vitamin D and become a more important source in winter when there are fewer daylight hours.
But dermatologists say we shouldn’t worry about sunscreen impacting our Vitamin D absorption as it doesn’t stop you getting your dose.
‘Studies have shown that sunscreen does not reduce vitamin D levels and preventing sunburn is crucial for maintaining skin health,’ stressed Dr Laftah.
Dr Kluck added: ‘We know we definitely need vitamin D and one of the ways we get it is through the action of UV on our skin, we can also get through diet and supplementation.’
But she explains the amount of sunlight you need to produce vitamin D does depend on your skin colour.
‘We know that particular groups are at higher risk of low UV, low vitamin D levels. So particularly people with brown and black skin, their skin needs more sun exposure to make vitamin D,’ Dr Kluck added.
For lighter skin types daily sunlight exposure for 10-15 minutes between April and September provides sufficient year-round vitamin D while also minimising the risks of sunburn and skin cancer. For darker skin types, 25-40 minutes is recommended, according to the British Skin Foundation.

However, just getting a tan is still an indicator of skin damage, experts warn.
Melanin is the natural pigment produced by the skin in response to the suns rays — responsible for producing a tan — that protect it from UV damage.
‘For people with lighter skin tones, there is a common misconception that you can build up a base tan which will protect you,’ said Dr Bav Shergill a consultant dermatologist at the Queen Victoria Hospital, London and spokesperson for the British Association of Dermatologists.
He added: ‘A tan is a reaction to sun damage, so to develop a base tan, you have to damage your skin.
‘Evidence also suggests that a “base tan” offers the equivalent of SPF 4 — not enough to provide meaningful protection.’
Dr Kluck added: ‘People used to consider a tan as an indicator of health.
‘Although we still may think a tan looks nice, it is still an indicator of damage to our skin and it is telling us our skin is having to generate more melanin because it’s trying to protect the DNA and our cells are sensing damage.
‘What is happening when we get a tan and when we get a sunburn is we are damaging DNA in our skin. We’re potentially setting ourselves up for getting mutations in our DNA that increases our cancer.’
Around 15,000 Brits and 100,000 Americans are diagnosed with melanoma, the most common form of skin cancer, each year.
This makes it the fifth most common cancer in the UK.
Additionally, melanoma rates in Britain have risen faster than any other common cancer.
Increased UV exposure from the sun bathing or tanning beds, has been blamed for the increase.
Despite huge strides forward in treatment that has seen survival leap from less than 50 per cent to more than 90 per cent in the past decade, melanoma still kills more than 2,000 people a year.
Melanoma is often fast growing and can quickly burrow through the skin and into the blood vessels beneath.
Once the cancer cells get into the bloodstream, the disease can the spread to other parts of the body.
Matthew Patey, chief executive officer of the British Skin Foundation said: ‘The skin is the body’s largest organ and looking after it is key.
‘If you could reduce the risk of other forms of cancer with such simple measures, it would be a no-brainer.
‘The message here is clear, more protection from harmful UV rays — whether with clothing, sunscreen or shade, ideally a combination of all three — reduces the risk of skin cancer in later life.’