Wellness
oi-Shivangi Karn
Every year on 19 June, World Sickle Cell Day is celebrated to raise awareness on this common, inherited blood disorder. According to the WHO, around five per cent of the world’s population carries the sickle cell gene and approximately 300000 babies are born every year with this disorder.
Children born with sickle cell disease (SCD) die sooner as their body is unable to produce (or produce very less) healthy haemoglobin. Cord blood banking or banking umbilical cord blood (blood left in the umbilical cord during the child’s birth) is the best way a family could secure the health of their child, in case the child is born with SCD or with other blood or immune system disorders.
 Leukaemia : Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Prevention And Treatment
Leukaemia : Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Prevention And Treatment
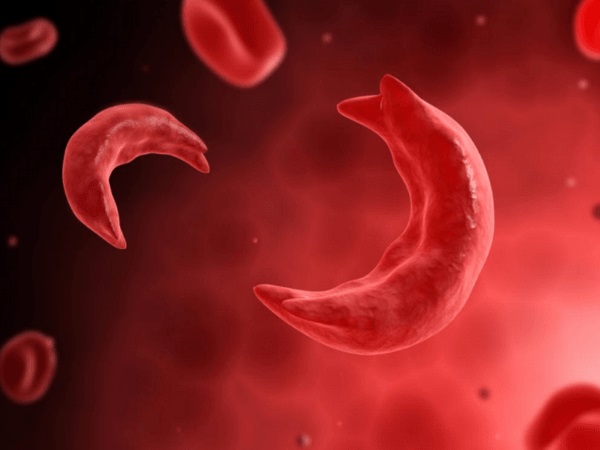
What Is Sickle Cell Disease?
Sickle cell diseases (SCD) is a chronic blood disorder characterised by an abnormality in haemoglobin, a protein found in the red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body. Usually, haemoglobin is round in shape but the presence of SC gene makes the red blood cells C-shaped, hard, sticky, fragile and prone to rupture.
The round-shaped haemoglobin carries more oxygen while the C-shaped ones carry less. As they are hard and sticky, they get stuck in blood vessels and block the passage. The body organs or tissues then suffer the lack of blood and oxygen and start functioning abnormally or dies.
The symptoms of SCD start coming within the five months of a child’s birth. This causes the child to die early. The treatment of SCD includes stem cell transplant or bone marrow transplant. Bone marrow is the spongy tissue that makes red blood cells. The genetic defect in them due to the sickle cell gene makes them produce sickle-shaped red blood cells. This makes cord blood transplant very important.
 Scoliosis Awareness Month: Importance Of Diet, Nutritional Tips And Yoga For People With Scoliosis
Scoliosis Awareness Month: Importance Of Diet, Nutritional Tips And Yoga For People With Scoliosis
READ RELATED: America’s Largest Grocery Chain Just Launched a New Budget-Friendly Line of Products

What Is Cord Blood Banking?
Umbilical cord blood contains the stem cells which can produce healthy blood cells. During the pregnancy, the umbilical cord provides nutrients to the baby from the food the mother eats. At the time of birth, the umbilical cord is cut as it is no longer needed by the baby.
The blood in the cord contains ten times more stem cells than those produced by the bone marrow. Usually, it gets thrown away, but if a family opts for cord blood banking, after the birth, the doctor collects around 40 ml of the blood from the umbilical cord and send it to the cord blood bank for testing and preservation. The process is painless and requires just a few minutes.
Cord blood is important because it is potentially capable of treating diseases such as leukaemia, aplastic anaemia, sickle cell diseases and other blood and immunodeficiency diseases. In future, it can help the child or any of his/her family members if they are diagnosed with the aforementioned diseases. You can also donate the cord blood if you wish.
 Beta-thalassemia: Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Treatment and Prevention
Beta-thalassemia: Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Treatment and Prevention

Pros Of Cord Blood Banking
- As aforementioned, it helps save lives and treat diseases related to the immune system and blood such as SCD.
- You will get access to cord blood whenever needed.
- The cord blood is very helpful for those with a family history of genetic diseases like SCD, leukaemia and others.
- Sometimes, a child’s cord blood does not match due to genetic mutation when he/she grows up. In this case, if there’s a large supply of cord blood, chances are someone else’s cord blood may match and save their life. This is why, every family are recommended for cord blood banking.
- There is a higher chance of cord blood match in a family, especially among siblings.
- Cord blood can also be used to treat other diseases apart from genetic conditions. Many studies are going on to find out the number of diseases it can treat. Some studies believe that one day the cord blood may be able to treat diseases like Parkinson’s diseases, breast cancer and others.
- No danger or pain is involved in the process.
 COVID-19 Severity In Patients With Haematological (Blood) Disease – Know What The Study Says
COVID-19 Severity In Patients With Haematological (Blood) Disease – Know What The Study Says

Cons Of Cord Blood Banking
- The cost of storing cord blood in private hospitals is very expensive. It also requires a high annual storage fee. This method is considered when a family has a history of genetic diseases. Private cord blood banking is done for personal usage in the future.
- In public cord banking, a family cannot opt for storage of cord blood for their personal use in the future. They can only opt for a donation to public hospitals. The hospital then reserves all the rights of the blood and gives it to someone in need. In case, you need the blood in the future, you have to contact the cord blood bank.
- Beyond 20 years, the stored cord blood does not guarantee its efficacy.
- If a private cord bank closes due to some reasons, the family have to search for another storage bank.
- The donor and receiver both have to meet certain criteria for donating as well as receiving cord blood.
- Private banks may discard the preserved blood when payment is not done on time.
- Sometimes, it is harder to find a hospital that works with public cord blood banks.
- Delay in collecting the umbilical cord blood may cause the blood to flow back to the child.
- There’s a very low chance that the cord blood will be used by the child in the future. It is 1 out of 400.

To Conclude:
Every year, many children die due to sickle cell disease. Therefore, to save them, opting for donating cord blood to public banks is the best thing one could do. If you have a family history of SCD, opt for preserving in the private blood banks to secure the future of your child and your family members.
GET THE BEST BOLDSKY STORIES!
Allow Notifications
You have already subscribed
Story first published: Friday, June 19, 2020, 7:00 [IST]
Source: boldsky blog



 17 Signs And Symptoms Of Iron Deficiency
17 Signs And Symptoms Of Iron Deficiency 15 Herbs and Spices In Cancer Prevention and Treatment
15 Herbs and Spices In Cancer Prevention and Treatment


















