Pineapple is a super sweet and tangy fruit that is synonymous with tropical and island vibes. Who doesn’t love a pina colada?! But besides being a main ingredient in the refreshing drink, it’s also packed with vitamins.
“Pineapple is an excellent source of vitamin C and low in calories,” says registered dietitian Jonathan Valdez, RDN, owner of Genki Nutrition and a spokesperson for the New York State Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
Nutritionally, it’s also an excellent source of fiber.
“Overall pineapple is an excellent source of vitamins and minerals,” says Keri Gans, MS, RDN, CDN, registered dietitian nutritionist and author of The Small Change Diet. “Pineapple also has 2.3 grams of fiber per one-cup serving, and fiber has been associated with increased satiety and weight management, as well as stabilizing blood sugars.” (Read more: One Major Effect of Eating Fiber-Rich Foods, Says Expert.)
If you love pineapple, you may be surprised by other ways it can impact your overall health. So we asked nutritional experts to share some surprising side effects of eating pineapple. Read on, and for more on how to eat healthy, don’t miss Eating Habits to Lose Abdominal Fat As You Age, Say Dietitians.


“Bromelain plays a role as a powerful anti-inflammatory, which one study showed a decrease in inflammatory mediators for individuals with IBD, that could potentially alleviate symptoms for patients suffering from IBD,” says Valdez. “However, more studies are needed to recommend bromelain as a treatment method for IBD.”


“This may be a reaction to a latex allergy,” says Gans. “Pineapple is a source of natural rubber latex. If known to have this allergy, an individual should not consume pineapple.”
READ RELATED: Get a Flatter Stomach at 50 With This Tummy-tightening Challenge
READ MORE: The Secret Drinking Trick to Reduce Inflammation, Says Expert


“Pineapple is packed with the antioxidant vitamin C which has anti-inflammatory properties that may help decrease joint pain caused by osteoarthritis, support immune health, and decrease the risk for heart disease,” says Gans.


“Although uncommon, some individuals sensitive to bromelain or who consume excessive amounts of pineapple report experiencing diarrhea and vomiting, but the reason why remains unknown,” says Valdez.
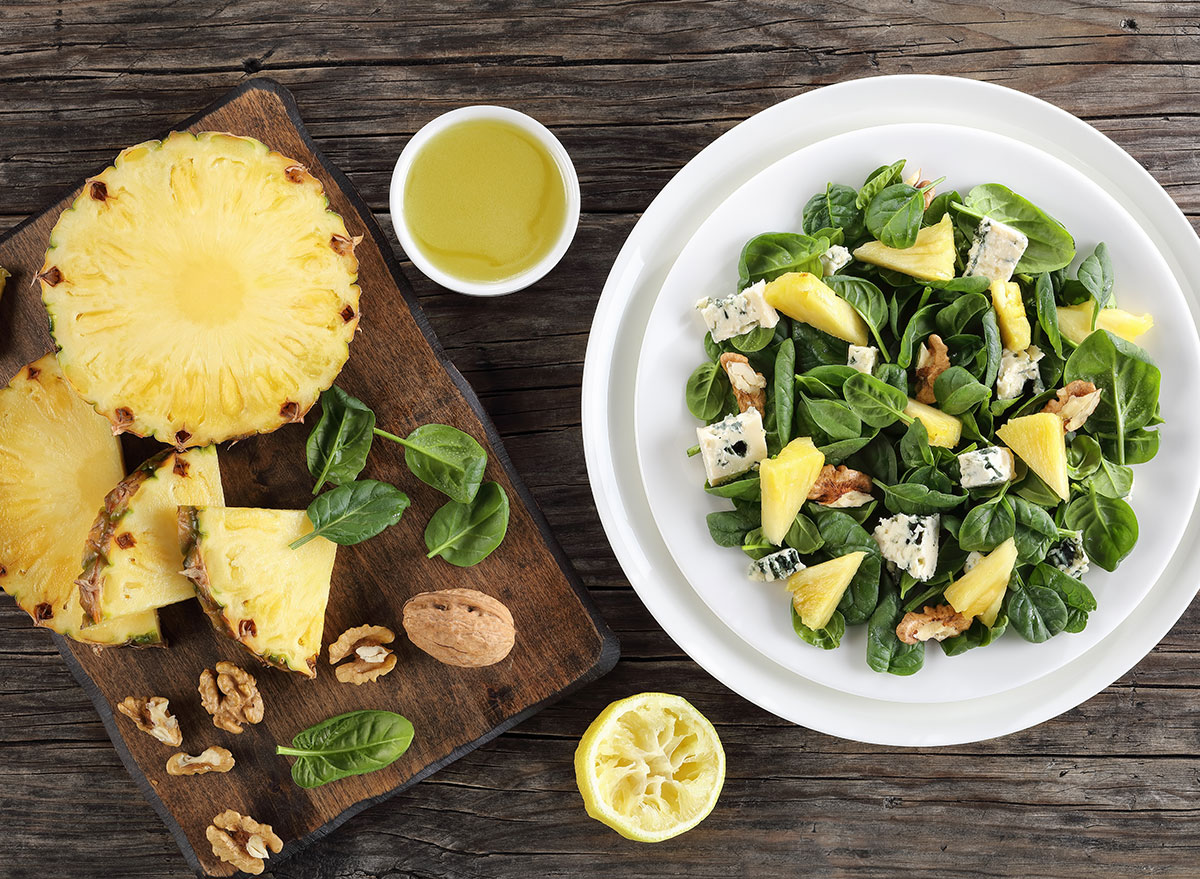


“Due to bromelain’s meat tenderizing properties, eating too much can cause tenderness of the mouth, lip, and tongue,” says Valdez. “Try cooking pineapple to break down bromelain and reduce these side effects. Also, avoid eating raw pineapple from the stem or core as the highest amount of bromelain is found there.”


“Pineapple is a good source of manganese, which is important for bone health,” says Gans.


“Bromelain contains anti-inflammatory properties that have been used to reduce pain and swelling from burns, joint pain, and other inflammatory diseases,” says Valdez.


“The enzymes in pineapple known as bromelain slow blood clotting, as well as increase red and white blood cells production, which leads to improved blood flow,” says Valdez.
Source: